Acidified Food Regulation (Subpart 114)
What you Need to Know:
If you are unsure of whether your product is an acidified food, see Introduction to Acid Foods
If you produce an acidified food, you must conduct additional filings with the FDA (free)
Producers of acidified foods must complete the "Better Process Control School" or an equivalent training course (available online)
Required Registrations/Filings for Acidified Food Producers
If you produce an acidified food, you must register your facility and file each acidified foods you process with the FDA.
Food Canning Establishment Registration
If you produce an acidified food, you must register the location where you produce that food. This filing is in addition to the normal food-facility-registration.
This filing simply notifies the FDA that acidified foods (which can be higher-risk food products) are being produced at this location. Completing this registration will not trigger an inspection.
File Electronically:Food Canning Establishment Registration (Form 2541).
File in Paper: Food Canning Establishment Registration (Form 2541)
If you have addition questions about completing Form 2541 see Instructions on Registering a Food Canning Establishment
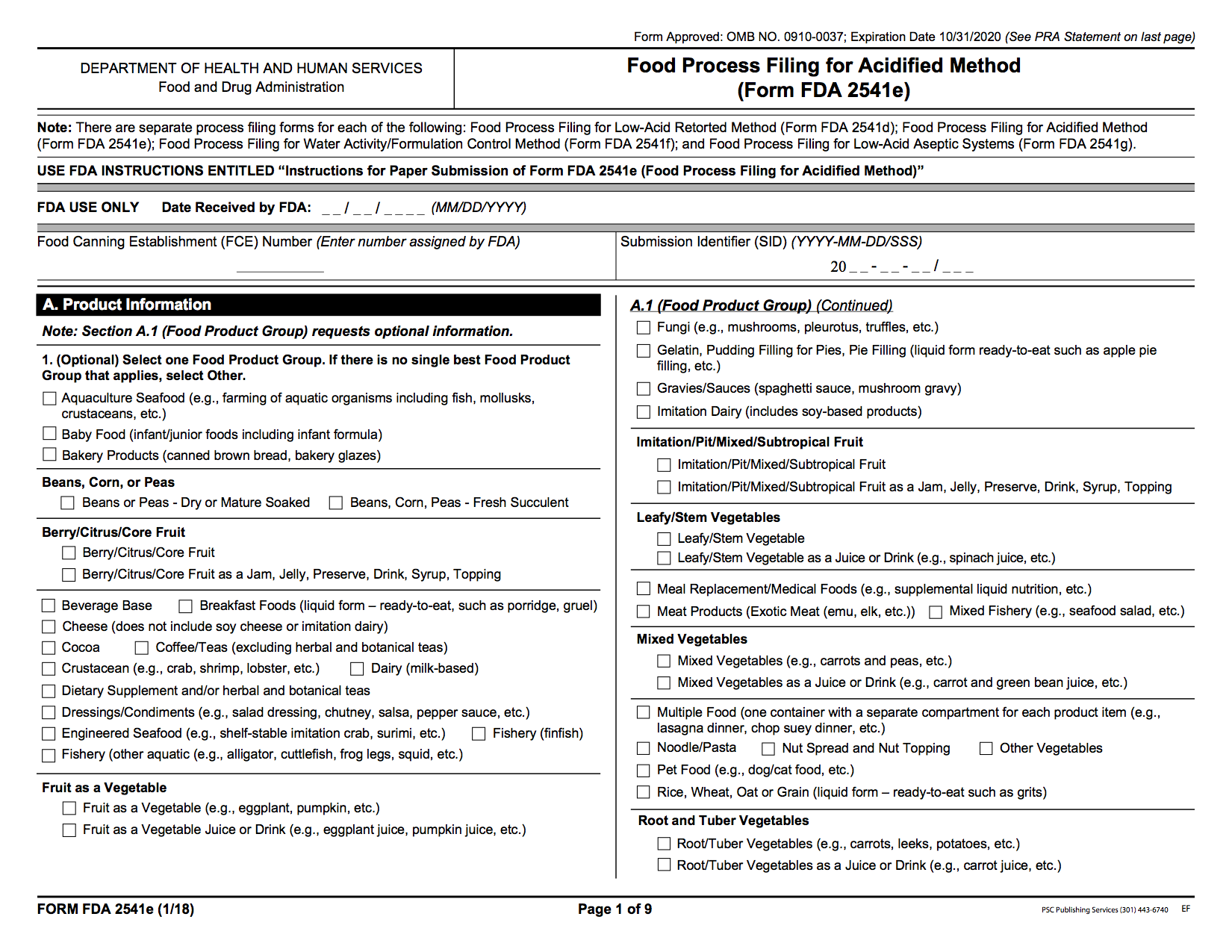
Food Process Filing for an Acidified Food
Paper Form: Food Process Filing for an Acidified Food (Form 2541e)
Producers of acidified foods must file a scheduled process for each acidified product that they produce. If a salsa company produces 5 SKUs that are all acidified foods, then they must submit 5 process filings, one for each SKU.
There is no requirement to file for products that do not fit the definition of an "acidified food".
File Electronically:Food Process Filing for an Acidified Food (Form 2541e)
File in Paper:Food Process Filing for an Acidified Food (Form 2541e)
If you have questions about the filing process, see Instructions on filing Form 2541e
Requirements for Processing Acidified Foods
Always follow your scheduled process and contact your process authority if something goes wrong.
Process and Controls
Scheduled Process
The manufacturer must follow a scheduled process.
The schedule process must be established by a person who as expert knowledge about the acidification and processing of acidified foods.
Processing Operations
The food must be thermally-processed (i.e. a heat-based kill step) to eliminate bacteria capable of reproducing in the finished product. Preservatives may be used in lieu of thermal processing for controlling the growth of microorganisms that are not harmful (i.e. spoilage bacteria that would ruin the food but not cause illness in humans).
Keep your production records onsite (digital is fine) for at least 3 years.
Acidification Procedures
Some acceptable methods used to acidify foods include:
Blanching ingredients in acidified solutions
Immersing blanched ingredients in acidified solutions
Directly adding a measured amount of acid solution into a batch of food.
Directly adding a measured amount of acid into individual containers during product.
Measuring pH
The equilibrium pH of the final product must be below 4.6 and it must reach this within the timeframe set in the scheduled process.
The pH of the product must be measured and recorded to maintain control throughout the process. If the final pH of the product is ≥4.0, then a potentiometric pH meter must be used (these are more accurate). If the final pH is <4.0, any type of pH meter may be used.
pH readings should be taken at a temperature of 20ºC-30ºC (68º-86ºF). Optimal temperature for pH test accuracy is 25ºC (77ºF).
For a full explanation of pH and testing methodology, see §114.90
Containers and Coding:
You must test and examine your containers to confirm that they protect your final product from leakage or contamination
Each container must be labeled with a code that specifies the following:
Where the product was packed
The contents of the container
The date of packing
The code must be changed for each personnel shift, at minimum.
Deviations from Scheduled Process
If the equilibrium pH is measured at >4.6 the processor must take one of the following steps:
Fully reprocess the food using a process approved by a process authority (this can be simply re-processing according to your usual method)
Thermally process the food as a low-acid-canned food
Set aside the food for evaluation by a process authority
Destroy the food.
Make a record of this incident, regardless of the outcome.
FAQ
Do I need to register my facility and products if I operate outside the US?
If you produce a product that meets the definition of an "acidified food" for consumption inside the US, then you must register your facility (Form 2541) and each of your acidified food products (2541e).
Processors located outside the US must also complete these registrations if their food will be exported for consumption inside the US.
Wholesalers, importers, distributors and brokers are not required to register and file processes
Does compliance with Subpart 114 exempt me from other requirements?
A business operating under Acidified Food Regulations ( Subpart 114 ) is still subject to the requirements in Subpart 117 B: Current Good Manufacturing Processes as it relates to determining whether a product is adulterated.